Mathematical Logic 7 Completeness 1
Before:久违的数理逻辑课!上了7节课终于觉得有点入门了,还是挺有意思的。周四下午闪击南京,周五下午又闪击回来。虽然只有1天,但很开心在这短短的20个小时内帮助了不少人(都是无意间)。我要永远做个善良的人!
Mathematical Logic 7 Completeness 1
我们继续完备性的证明!
我们知道,要证明一阶逻辑的完备性,我们只需要证明:
Given a consisitent ,it suffices to construct a term model = () such that:
\iff .
昨晚室友问我为了体现完备性,就是要证明 , 难道不是在说对于任何一个 上的模型,都能使为真吗?但是这里不是只找了一个模型吗?我想这应该是由于Henkin’s Term Model的特殊性,但这个留到后几节课再讨论了。
Henkin’s Term Model Recall 模型回顾
首先引入等价类的概念:
Let $ t_1,t_2 $ .Then $ t_1 $ ~ $ t_2 $ if .
For every t we define:
:= {t’ |t’ ~ t}
Definition
The term structure for (\Phi), denoted by (\mathfrak{I}^{\Phi}), is defined as follows.
-
Universe:
-
Relation symbols:
For every \(n\)-ary relation symbol \(R \in S\), and \(\overline{t_1}, \ldots, \overline{t_n} \in T^{\Phi}\),
-
Function symbols:
For every \(n\)-ary function symbol \(f \in S\), and \(\overline{t_1}, \ldots, \overline{t_n} \in T^{\Phi}\),
-
Constants:
For every constant \(c \in S\),
For every variable ,we let:
\mathfrak{\beta}^{\Phi}\(v_i\) :=
对于原子公式成立 atomic
Lemma 5
(i) For any \( t \in T^S \),
(ii) For every atomic \(\varphi\),
\mathfrak{I}^\Phi \models \varphi \iff \Phi \vdash \varphi.
(i)的证明,我们对项t进行归纳:
- t = is a variable
- t = c is a constant
- t = f
根据定义可证
(ii)的证明,对2个原子公式进行分类讨论:
利用(i)中所证,可证
Consistent,Negation Complete,Contains Witness
Lemma 8
先看一个引理:
Lemma 8
Let (\varphi) be an (S)-formula and (x_1, \ldots, x_n) pairwise distinct variables. Then
(i)
if and only if there are (S)-terms (t_1, \ldots, t_n) such that
(ii)
if and only if for all (S)-terms (t_1, \ldots, t_n) we have
由替换引理等可证
Consistent
Definition
is consistent if there is no such that both ⊢ and ⊢ . Otherwise, is inconsistent.
Negation Complete
Definition
A set (\Phi) is negation complete if for every (S)-formula (\varphi):
通俗的说,就是如果 证不出来,那就一定能证出来;证不出来,那就一定能证出来
Contains Witness
Definition
🔍 A set contains witnesses if for every and every variable , there exists a term such that:
Henkin’s Theorem Proof
First,还是先来证明一个引理:
Lemma 9
Assume that is consistent, negation complete, and contains witnesses. Then for all -formulas and :
(i)
if and only if \Phi \not\vdash \neg \varphi.
(ii)
if and only if or .
(iii)
if and only if there is a term such that .
(i)向右通过consistent定义说明,向左通过negation complete定义说明
(ii)向左利用V-intro by succedent证明,向右证明如下:
Assume that
Proof Steps:
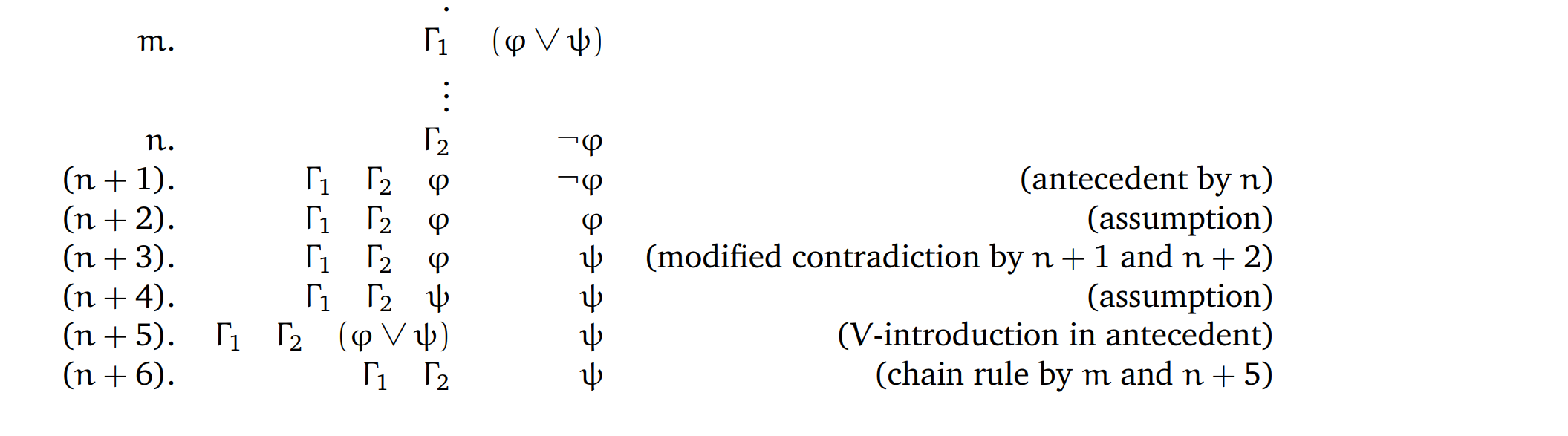
(iii)向右可通过Modus ponens证明,向左可通过\exist-intro in succedent证明
Henkin’s Theorem
由引理证明起来还是比较显然的:
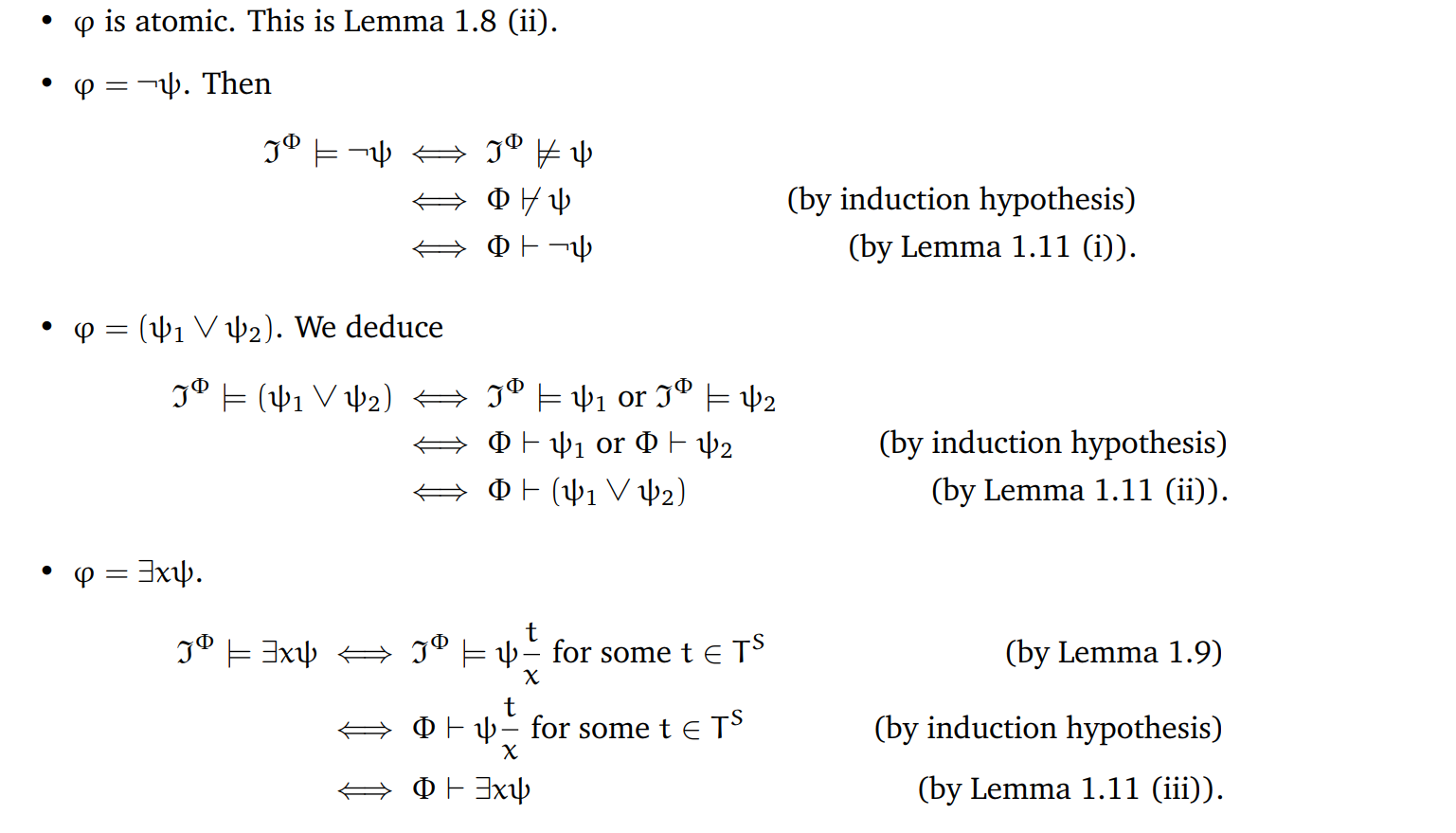
注意,这里对公式的归纳是对公式的connective rank归纳,保证要证的公式都更长:
Rank Definition:
rk(\varphi) :=
\begin{cases}
0 & \text{if } \varphi \text{ is atomic,} \
1 + rk(\psi) & \text{if } \varphi = \neg\psi, \
1 + rk(\psi_1) + rk(\psi_2) & \text{if } \varphi = (\psi_1 \lor \psi_2), \
1 + rk(\psi) & \text{if } \varphi = \exists x \psi.
\end{cases}